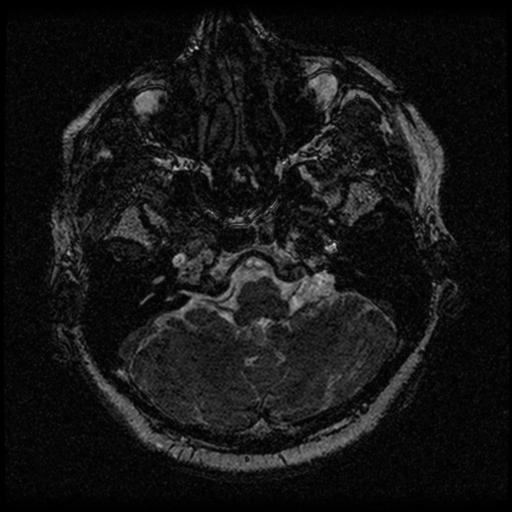
File:Acoustic schwannoma (Radiopaedia 33045-34060 Axial T2 9).png
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Acoustic_schwannoma_(Radiopaedia_33045-34060_Axial_T2_9).png (512 × 512 pixels, file size: 254 KB, MIME type: image/png)
Summary:
- Radiopaedia case ID: 33045
- Image ID: 9999280
- Image stack position: 9/72
- Plane projection: Axial
- Aux modality: T2
- Study findings: There is a avidly enhancing extra-axial mass lesion within the right cerebello-pontine angle. On current imaging, the mass demonstrates isointense signal to adjacent cerebellum on T1-weighted imaging and low signal on FIESTA and B0 sequences. The lesion appears to be closely applied to the posterior margin of the right internal auditory canal with a thin rind of enhancing tissue extending 3mm along the dorsal wall of the right internal auditory canal. The cisternal segment of the right CN7/8 complex is indistinguishable from the tumor, however, the intra-canalicular segments of the nerves appear to be separate from the tumor. The tumor causes mass effect on the adjacent right cerebellar hemisphere and right brachium pontis with mildly increased FLAIR signal within the right middle cerebellar peduncle. There are no remote intra- or extra-axial mass lesions, acute hemorrhages or collections. No acute infarcts. The left cerebello-pontine angle and left middle and inner ear structures image normally. Conclusion: Based on MRI features, the differential for the right cerebello-pontine angle mass lesion continues to include both meningioma and vestibular schwannoma - vestibular schwannomas are more common and remain the more likely differential.
- Modality: MRI
- System: Central Nervous System
- Findings: A round, homogeneous extra-axial mass centered on the right cerebellopontine angle displaces the pons and the middle cerebral peduncle to the left and distorts but does not efface the fourth ventricle. The mass enhances homogeneously and vividly. There is minimal extension into the right porus acusticus and minimal widening of the right internal auditory canal compared to the left. No underlying hyperostosis. No other enhancing lesions identified. No hydrocephalus. No intra or extra axial hemorrhage. No evidence of acute ischemia. Conclusion: Appearances of the right cerebellar pontine angle mass are those of either a meningioma or acoustic neuroma. On the basis of this CT it is difficult to distinguish between the two.
- Published: 4th Jan 2015
- Source: https://radiopaedia.org/cases/acoustic-schwannoma-19
- Author: Frank Gaillard
- Permission: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
Licensing:
Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported (CC BY-NC-SA 3.0)
File history
Click on a date/time to view the file as it appeared at that time.
| Date/Time | Thumbnail | Dimensions | User | Comment | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| current | 03:02, 2 April 2021 |  | 512 × 512 (254 KB) | Fæ (talk | contribs) | Radiopaedia project rID:33045 (batch #490-9 A9) |
You cannot overwrite this file.
File usage
The following page uses this file: